

岭南现代临床外科 ›› 2020, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (02): 161-166.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-976X.2020.02.006
摘要:
直肠癌是常见的恶性实体肿瘤,肿瘤的转移常使患者失去完全切除肿瘤的手术机会,降低了直肠癌的预后[1]。针对肿瘤转移机制的研究十分重要。已知组织金属蛋白酶抑制剂-1(tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1,TIMP1)存在两种作用模式,一方面,TIMP1通过结合膜受体CD63激活胞内通路,从而发挥生物学功能[2-4];另一方面,TIMP1作为金属蛋白酶(metalloproteinases,MMPs)的抑制剂被人们熟知,TIMP1与MMPs之间的动态平衡,维持着细胞外基质的稳定,与肿瘤转移密切相关[5,6]。有文献报道,胃癌中,TIMP1 与 SERPINE1相关,而SERPINE1与EMT密切相关,TIMP1影响SERPINE1从而影响肿瘤转移[7]。TIMP1在多种肿瘤中高表达,且因其与预后密切相关,还可作为肿瘤预后的预测因子[8-11]。然而,TIMP1在直肠癌中的表达水平及是否能预测直肠癌转移与预后研究较少。
EFEMP1是纤维蛋白糖蛋白家族中的一员,其主要功能是维护基膜稳定性及细胞外基质完整性。有文献报道,在肺癌、肝癌和鼻咽癌中,EFEMP1可抑制肿瘤的侵袭和转移,其表达水平与肿瘤预后相关,可作为肿瘤的预测因子[12-14]。在宫颈癌和骨肉瘤中,EFEMP1可通过诱导EMT从而促进肿瘤转移[15,16]。然而 EFEMP1在直肠癌中的研究相对较少。
本研究旨在探讨TIMP1在直肠癌中的表达水平,以及TIMP1表达量在不同临床分期间的差异,探讨TIMP1与直肠癌预后的关系。探讨与TIMP1相关的差异基因的分子功能及生物学功能。从而探讨TIMP1与EFEMP1的相关性,以及EFEMP1在直肠癌中的表达水平及与预后的关系。
直肠癌癌旁组织与癌组织各个基因表达量及临床资料来自于癌症基因组图谱(the cancer genome atlas,TCGA)。
分析正常组织与直肠癌组织不同临床分期间的TIMP1的表达差异,分析TIMP1表达水平与直肠癌患者总体生存时间与无瘤生存时间之间的关系。利用 Decenter,参数设置为 log2FC>1,FDR<0.05,筛选正常组织与直肠癌组织的差异基因,绘制火山图。根据TIMP1的表达量,将直肠癌患者分为TIMP1高表达组与TIMP1低表达组,利用Decenter,参数设置为log2FC>1,FDR<0.05,筛选两组的差异基因,绘制火山图与热图。将差异基因进行基因富集分析,利用FUNRICH进行细胞成分(cellular component,CC),分子功能(molecular function,MF),生物过程(biological process,BP),生物通路(biological pathway)分析。寻找与TIMP1功能可能密切相关的基因,利用Origin 2018分析TIMP1与EFEMP1的相关性。分析EFEMP1表达水平与直肠癌患者总体生存时间与无瘤生存时间之间的关系。
TIMP1的表达水平经四分位数分成四等份并绘制箱式图进行比较,数据以中位数(四分位间距)表示,采用T检验与秩和检验。使用Kaplan-Meier生存分析来绘制OS及PFS曲线,并采用Logrank检验比较不同表达水平的生存差异从而得出P值。
如图1A所示,TCGA数据库中10例直肠正常组织TIMP1表达量为51.03(42.58,59.40),165例直肠癌组织中TIMP1表达量为174.39(130.71,242.09)。直肠癌组织中TIMP1表达量高于正常组织(P<0.05)。如图1B所示,30例Ⅰ期患者TIMP1表达量 152.48(107.13,203.03),50例Ⅱ期患者TIMP1表达量 176.84(130.73,235.22),51例Ⅲ期患者 TIMP1表达量 195.35(133.00,296.44),24例Ⅳ期患者 TIMP1表达量 185.65(144.92,223.03)。Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ期直肠癌组织中TIMP1水平均明显高于正常组织(P<0.05),而各分期之间TIMP1表达水平无统计学意义(P>0.05)。生存曲线分析显示,TIMP1高表达患者OS与PFS均明显低于低表达患者(P<0.05)(图1C、D)。

图1 TIMP1在正常组织与直肠癌中的表达情况及与预后的关系
A.TIMP1在直肠癌组织中表达量高于正常组织;B.直肠癌不同临床分期的TIMP1表达均高于正常组织;C.TIMP1高表达患者总体生存时间低于低表达患者;D.TIMP1高表达患者无瘤生存时间低于低表达患者
将患者分为TIMP1高表达组与低表达组,筛选出差异基因,随后绘制火山图(图2A)。将差异基因进行基因富集分析。细胞成分分析结果显示,差异基因大多表达细胞外蛋白,与细胞外基质密切相关(图3A)。分子功能分析结果显示,差异基因表达蛋白主要参与构成细胞外基质的组成结构,细胞黏附分子活动,细胞生长活动,蛋白抑制活动,钙离子结合等(图3B)。生物过程分析结果显示,差异基因表达蛋白主要参与细胞生长过程,信号传导过程等(图3C)。生物通路分析结果显示,差异基因主要与EMT通路相关(图3D)。在TIMP1高表达组与低表达组的差异基因中,选取与EMT相关的23个基因,绘制热图(图2B)。筛选出差异基因筛选在正常组织与直肠癌组织中存在表达差异的基因,绘制火山图(图2C)。综合筛选出9个,在正常组织与直肠癌组织中存在表达差异,且与TIMP1相关的EMT相关基因:EFEMP1、Fibulin-1(FBLN1)、生长停滞特异性1(growth arrest specific 1,GAS1)、双糖链蛋白多糖(biglycan,BGN)、视黄酸受体应答蛋白 2(Retinoic acid receptor responder protein 2,RARRES2)、泛素羧基末端水解酶L1(Ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1,UCHL1)、前列环素合酶(prostacyclin synthase,PTGIS)、耳蜗背核(the dorsal cochlear nucleus,DCN)、细胞色素P450 1B1(Cytochrome P450 1B1,CYP1B1)。
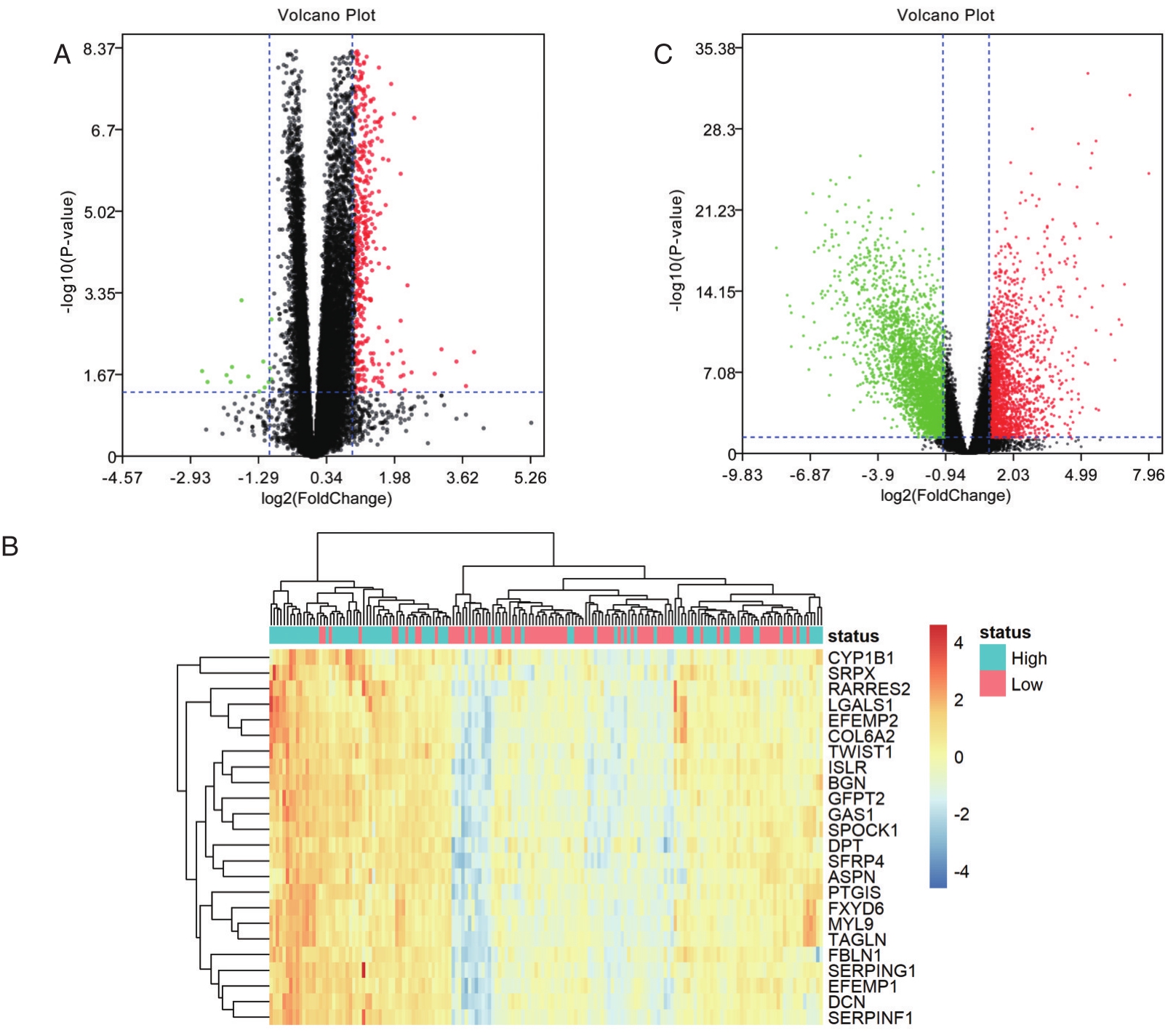
图2 差异基因的筛选
A.TIMP1高表达组与TIMP1低表达组差异基因的火山图;B.TIMP1高表达组与TIMP1低表达组差异基因中与EMT相关的基因的热图;C.正常组织与直肠癌组织差异基因的火山图
如图4A所示,EFEMP1随着TIMP1表达量升高而降低,EFEMP1与TIMP1呈正相关相关(r=0.2795,P<0.05)。如图4B所示,EFEMP1高表达患者总体生存时间低于低表达患者(P<0.05)。如图4C所示,EFEMP1高表达患者无瘤生存时间低于低表达患者(P<0.05)。
本研究结果显示直肠癌组织中TIMP1表达水平高于正常组织,不同临床分期直肠癌组织均高于正常组织。TIMP1高表达组预后差于TIMP1低表达组,验证了此前报道的TIMP1为结直肠癌的标记物。基因富集分析显示,根据TIMP1表达量筛选出的差异基因,其功能与细胞外基质的稳定性及EMT相关。EMT指上皮来源的肿瘤细胞发生基因或表观遗传水平改变,上皮标志物表达下降,间质标志物表达上调,失去细胞间紧密连接和细胞极性,获得间质细胞特性,形态转变为梭形,迁移和侵袭能力增强。一方面,TIMP1可阻断MMPs的功能,从而维持细胞外基质的稳定性,进而抑制肿瘤转移。另一方面,TIMP1还可与SERPINE1等EMT相关分子相互作用,从而影响肿瘤细胞EMT,促进肿瘤的转移。

图3 TIMP1高表达组与TIMP1低表达组差异基因的基因富集
A.差异基因的细胞成分分析;B.差异基因的分子功能分析;C.差异基因的生物过程分析;D.差异基因的生物通路分析
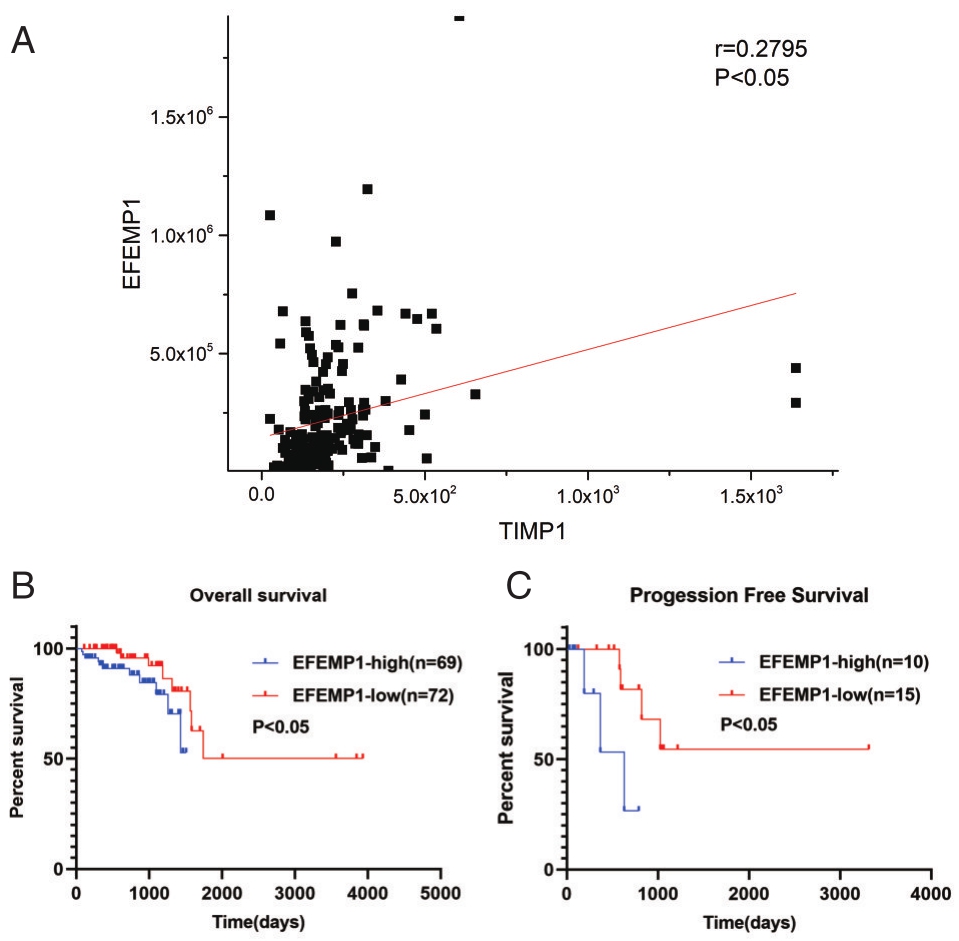
图4 TIMP1与EFEMP1的关系及EFEMP1与直肠癌预后的关系 A.TIMP1与EFEMP1呈正相关;B.EFEMP1高表达患者总体生存时间低于低表达患者;C.EFEMP1高表达患者无瘤生存时间低于低表达患者
在根据TIMP1表达量筛选出的差异基因中,进一步筛选出在正常组织与直肠癌组织中存在表达差异的基因。最后得到9个基因:EFEMP1、FBLN1、GAS1、BGN、RARRES2、UCHL1、PTGIS、DCN、CYP1B1。其中,EFEMP1与EMT密切相关,一方面,在骨肉瘤等肿瘤中,敲低EFEMP1可上调E-钙黏素(E-cadherin)表达,抑制N-钙黏素(N-cad-herin)、波形蛋白(Vimentin)、Snail、Slug和Twist的表达,从而促进肿瘤细胞EMT,促进肿瘤的转移。另一方面,在子宫内膜癌等肿瘤中,EFEMP1与E-cadherin呈正相关,与Vimentin,Snail and β-catenin呈负相关[17]。本研究结果显示,在直肠癌组织中,EFEMP1高表达患者OS与PFS均明显低于低表达患者。说明EFEPM1在直肠癌中可能通过促进EMT起到促进肿瘤转移的功能。EFEPM1与直肠癌预后相关,可将EFEPM1作为直肠癌标志物,预测直肠癌患者预后情况。结果显示TIMP1在直肠癌中高表达,且TIMP1与EFEMP1存在正相关,说明可能存在TIMP1激活EFEMP1的表达从而促进EMT,进而促进直肠癌的转移,此假设有待进一步基础实验研究证实。
表1 TIMP1表达水平与临床资料
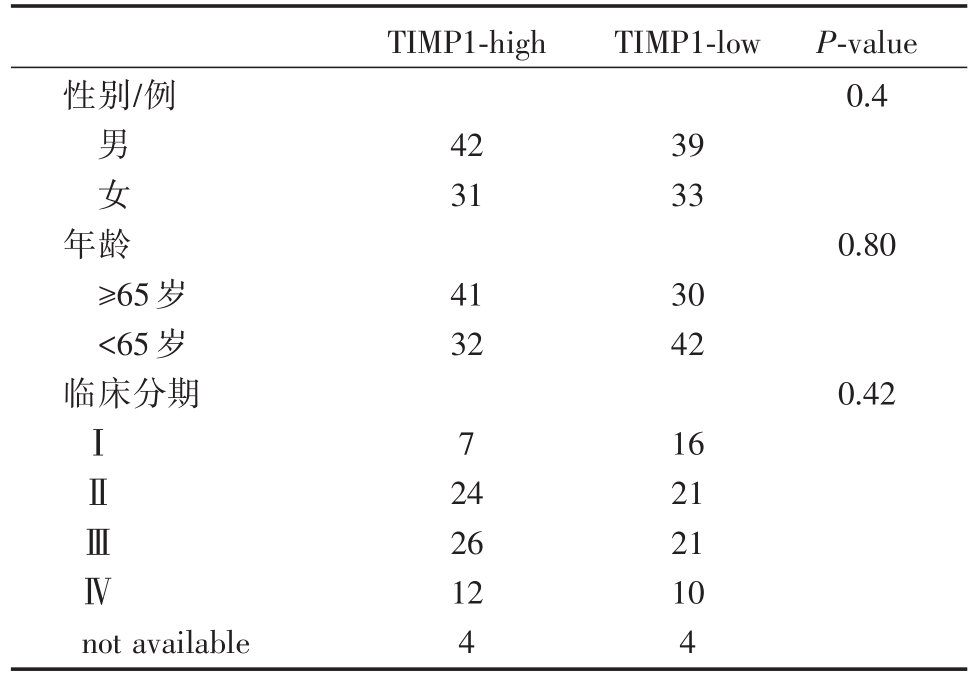
TIMP1-high TIMP1-low性别/例P-value 0.4男女42 31 39 33年龄≥65岁<65岁临床分期0.80 41 32 30 42 0.42ⅠⅡⅢⅣ7 not available 24 26 12 4 16 21 21 10 4
表2 TIMP1高表达组与低表达组的差异基因中与EMT相关的部分基因
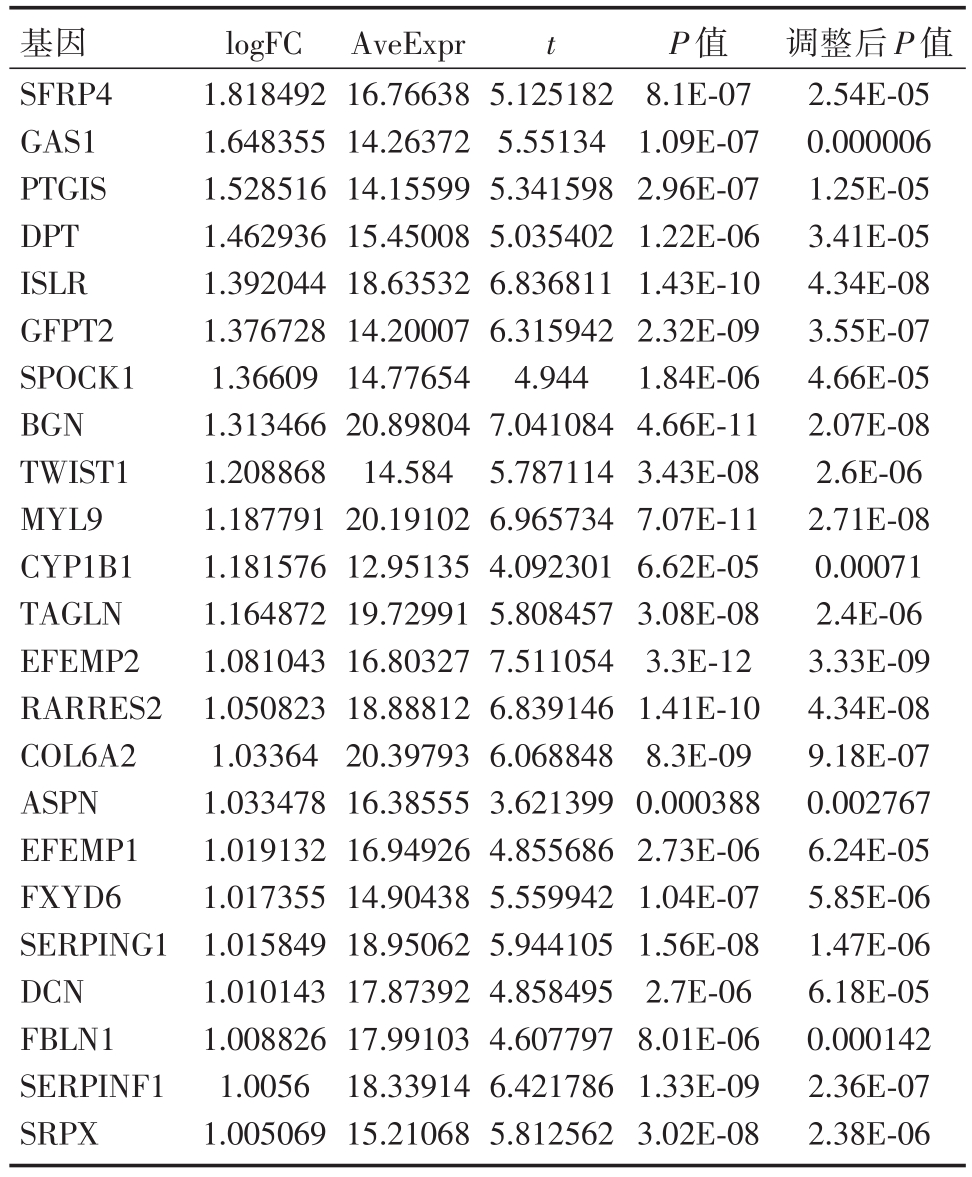
基因SFRP4 GAS1 PTGIS DPT ISLR GFPT2 SPOCK1 BGN TWIST1 MYL9 CYP1B1 TAGLN EFEMP2 RARRES2 COL6A2 ASPN EFEMP1 FXYD6 SERPING1 DCN FBLN1 SERPINF1 SRPX logFC 1.818492 1.648355 1.528516 1.462936 1.392044 1.376728 1.36609 1.313466 1.208868 1.187791 1.181576 1.164872 1.081043 1.050823 1.03364 1.033478 1.019132 1.017355 1.015849 1.010143 1.008826 1.0056 1.005069 AveExpr 16.76638 14.26372 14.15599 15.45008 18.63532 14.20007 14.77654 20.89804 14.584 20.19102 12.95135 19.72991 16.80327 18.88812 20.39793 16.38555 16.94926 14.90438 18.95062 17.87392 17.99103 18.33914 15.21068 t 5.125182 5.55134 5.341598 5.035402 6.836811 6.315942 4.944 7.041084 5.787114 6.965734 4.092301 5.808457 7.511054 6.839146 6.068848 3.621399 4.855686 5.559942 5.944105 4.858495 4.607797 6.421786 5.812562 P值8.1E-07 1.09E-07 2.96E-07 1.22E-06 1.43E-10 2.32E-09 1.84E-06 4.66E-11 3.43E-08 7.07E-11 6.62E-05 3.08E-08 3.3E-12 1.41E-10 8.3E-09 0.000388 2.73E-06 1.04E-07 1.56E-08 2.7E-06 8.01E-06 1.33E-09 3.02E-08调整后P值2.54E-05 0.000006 1.25E-05 3.41E-05 4.34E-08 3.55E-07 4.66E-05 2.07E-08 2.6E-06 2.71E-08 0.00071 2.4E-06 3.33E-09 4.34E-08 9.18E-07 0.002767 6.24E-05 5.85E-06 1.47E-06 6.18E-05 0.000142 2.36E-07 2.38E-06
表3 EFEMP1表达水平与临床资料
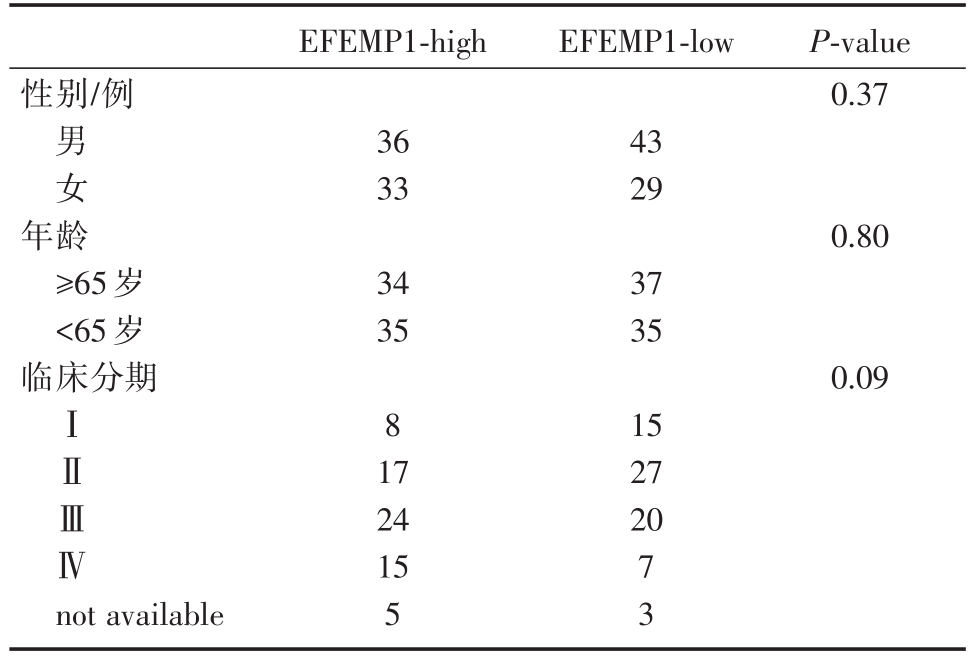
EFEMP1-high EFEMP1-low性别/例P-value 0.37男女36 33 43 29年龄≥65岁<65岁临床分期0.80 34 35 37 35 0.09ⅠⅡⅢⅣ8 15 27 20 not available 17 24 15 5 7 3
综上,TIMP1在直肠癌中高表达,且与预后呈负相关。EFEPM1与预后呈负相关。而TIMP1与EFEPM1存在相关性。TIMP1与EFEPM1可作为直肠癌的标记物及预测因子。
[1] Lord AC,Knijn N,Brown G,Nagtegaal ID.Pathways of spread in rectal cancer:a reappraisal of the true routes to distant metastatic disease[J].Eur J Cancer,2020,128:1-6.
[2] Toricelli M,Melo FH,Peres GB,et al.Timp1 interacts with beta-1 integrin and CD63 along melanoma genesis and confers anoikis resistance by activating PI3-K signaling pathway independently of Akt phosphorylation[J].Mol Cancer,2013,12:22.
[3] Forte D,Salvestrini V,Corradi G,et al.The tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1(TIMP-1)promotes survival and migration of acute myeloid leukemia cells through CD63/PI3K/Akt/p21 signaling[J].Oncotarget,2017,8(2):2261-2274.
[4] Lee SY,Kim JM,Cho SY,et al.TIMP-1 modulates chemotaxis of human neural stem cells through CD63 and integrin signalling[J].Biochem J,2014,459(3):565-576.
[5] Robert S,Gicquel T,Victoni T,et al.Involvement of matrix metalloproteinases(MMPs)and inflammasome pathway in molecular mechanisms of fibrosis[J].Biosci Rep,2016,36(4).
[6] Wang JC.Importance of Plasma Matrix Metalloproteinases(MMP)and Tissue Inhibitors of Metalloproteinase(TIMP)in development of fibrosis in agnogenic myeloid metaplasia[J].Leuk Lymphoma,2005,46(9):1261-1268.
[7] Satoh K,Hamada S,Shimosegawa T.Involvement of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in the development of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma[J].J Gastroenterol,2015,50(2):140-146.
[8] Wang YY,Li L,Zhao ZS,Wang HJ.Clinical utility of measuring expression levels of KAP1,TIMP1 and STC2 in peripheral blood of patients with gastric cancer[J].World J Surg Oncol,2013,11:81.
[9] Fernandez-Garcia B,Eiró N,Marín L,et al.Expression and prognostic significance of fibronectin and matrix metalloproteases in breast cancer metastasis[J].Histopathology,2014,64(4):512-522.
[10] Birgisson H,Nielsen HJ,Christensen IJ,et al.Preoperative plasma TIMP-1 is an independent prognostic indicator in patients with primary colorectal cancer:A prospective validation study[J].Eur J Cancer,2010,46(18):3323-3331.
[11] Laitinen A,Hagström J,Mustonen H,et al.Serum MMP-8 and TIMP-1 as prognostic biomarkers in gastric cancer[J].Tumour Biol,2018,40(9):1010428318799266.
[12] Hu J,Duan B,Jiang W,et al.Epidermal growth factor-containing fibulin-like extracellular matrix protein 1(EFEMP1)suppressed the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by promoting Semaphorin 3B(SEMA3B)[J].Cancer Med,2019,8(6):3152-3166.
[13] 郎媛媛,孟洁,宋晓萌,陈小军.EFEMP1通过下调MMP-7表达抑制肺癌细胞生长和侵袭[J].中国肺癌杂志,2015,18(2):92-97.
[14] Hwang C,Chien C,Huang S,et al.Fibulin-3 is associated with tumour progression and a poor prognosis in nasopharyngeal carcinomas and inhibits cell migration and invasion via suppressed AKT activity[J].J Pathol,2010,222(4):367-379.
[15] Wang S,Zhang D,Han S,et al.Fibulin-3 promotes osteosarcoma invasion and metastasis by inducing epithelial to mesenchymal transition and activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway[J].Sci Rep,2017,7(1):6215.
[16] Li J,Qi C,Liu X,et al.Fibulin-3 knockdown inhibits cervical cancer cell growth and metastasis in vitro and in vivo[J].Sci Rep,2018,8(1):10594.
[17] Yang T,Zhang H,Qiu H,et al.EFEMP1 is repressed by estrogen and inhibits the epithelial-mesenchymal transition via Wnt/β-catenin signaling in endometrial carcinoma[J].Oncotarget,2016,7(18):25712-25725.
Expression level and prognostic significance of TIMP1 and EFEMP1 in rectal cancer
中图分类号: