

岭南现代临床外科 ›› 2019, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (06): 732-741.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-976X.2019.06.020
孙晓旭
SUN Xiaoxu
摘要:
胫骨平台与股骨髁在多群肌肉、韧带的参与下构成了稳固的膝关节,是人体下肢力学传导的枢纽。较稳固的膝关节胫骨平台的脱位与骨折,多数原因是高能量暴力所致,发病率在高龄人群中已达 8%[1,2]。目前,胫骨平台骨折依据 Schatzker分型包含6个类型中,胫骨内侧平台骨折伴骨折脱位属于Ⅳ型骨折,占6个类型中的10%左右,患者骨折后,多出现膝关节半脱位合并半月板或腓侧副韧带损伤,同时伴有腘窝内神经、血管等结构损伤,即使手术治疗后,也会残留膝关节活动度降低,关节炎及畸形愈合或移位等并发症的出现,少数患者需施全膝关节置换二次手术[3,4]。当前对于此类型复杂的骨折尚缺乏的成熟的治疗方法和统一康复方案[5]。为选择合适的治疗方法,提高此类骨折患者的治疗效果,本文对胫骨平台骨折Ⅳ型骨折进行2种术式治疗,分析比较治疗效果,旨在为临床手术提供有效治疗方案。
选取2009年8月~2016年8月河南省鹤壁市人民医院收治的胫骨内侧平台骨折伴骨折脱位患者54例(男39,女15),年龄18~60周岁。受伤原因:交通伤24例,坠落伤18例,压砸伤12例,均为闭合性骨折,均无血管神经损伤或骨筋膜室综合征发生。合并有以下结构损伤:半月板10例,前后交叉韧带14例,胫侧和腓侧副韧带8例。纳入标准:①术前影像学检查确诊为:胫骨内侧平台骨折伴骨折脱位Ⅳ型;②膝关节部位均无手术史或严重外伤史;③均无心、肝、肺疾患与凝血系统功能障碍,均无糖尿病或严重营养不良等的相关疾病;④所有患者均由同一医生主刀手术,依据不同的手术方式分为两组:双钢板组患者29例,接受双钢板内侧手术入路+内固定治疗;单钢板组患者25例,接受前内侧入路+钢板联合前后位拉力螺钉固定治疗。患者对治疗方案签署知情同意书。患者一般情况和分型,表1。
进一步完善患者影像学检查资料,全面掌握膝关节骨折具体形态部位及其比邻结构损伤情况。术前准备,用石膏托或支具将患者下肢临时固定,避免患肢部位二次损伤。采用止痛活血和消肿等治疗,置患肢高抬姿势,待消肿后,再实施手术治疗。
表1 两组手术患者一般情况与分型
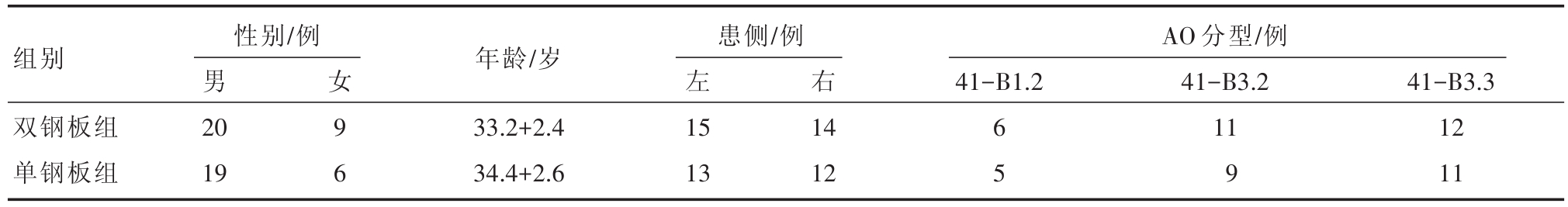
注:两组差异无统计学意义,P>0.05
组别 年龄/岁AO分型/例41-B1.2女 9 6性别/例男20 19患侧/例左15 13右双钢板组单钢板组33.2+2.4 34.4+2.6 14 12 6 5 41-B3.2 11 9 41-B3.3 12 11
两组患者均仰卧体位,屈膝45°,硬膜外麻醉,气囊止血带止血。于膝关节内侧“弧形”切口:由股骨内收肌结节起,“弧形”切至胫骨内侧骨嵴,向下10 cm左右,于股薄肌前方,钝型分离和牵开隐神经主干。双钢板组患者的手术方法:患者伸膝,复位骨折块后,先用克氏针固定,将患肢屈膝45°,然后牵开缝匠肌、股薄肌及半腱肌的联合肌腱膜,在腱膜下方安装一块内侧T形钢板,继续向下方分离和牵开半腱肌,用一块T形或L形钢板固定于胫骨内髁后方内。单钢板组患者的手术方法:前内侧入路,“钢板(T形或L形)联合拉力螺钉(前后位)”的固定方法,即内侧髁用T形或L形钢板固定,结合拉力螺钉固定前后位,注意拉力螺钉固定螺纹一定大于骨折线。术后,抬高2组患者患肢,48 h后拔除引流管,约72 h后,患肢膝关节结合CPM康复机适度活动;手术3月后定期复查,依据患肢恢复情况,指导患者下肢部分负重或完全负重。
分别记录和比较两组术式膝关节以下情况:①患者围手术期的入院时间、手术时间及术中出血量;②两组患者膝关节功能恢复情况,依据Harris评分量表[6]以及 Rasmussen放射学评分标准[7]进行比较;③测量和比较术后胫骨平台后倾角(PTSA)及内翻角(MPTA);④术后出现并发症情况。
采用SPSS 19.00软件统计学分析。计量资料用(x±s)表示,采用t检验,等级资料采用秩和检验,设定0.05检验标准为:当P<0.05时,以P<0.05为组间差异有统计学意义。
两组患者手术全过程顺利完成,比较住院时间、手术时间及术中出血量,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。Harris量表评分比较结果:术前和术后1 d,两组间量表评分,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);术后3个月,不同时间节点间两组量表评分,两组差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。Rasmussen放射学评分结果比较:术前,两组患者评分差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);术前不同时间点间差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);术后1 d和术后3个月,双钢板组评分明显高于单钢板组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。两组患者术后胫骨平台后倾角及内翻角测量结果:术后1 d与术后3个月,双钢板组患者胫骨平台后倾角及内翻角比较,均明显优于单钢板组(P<0.05)(表2)。
表2 两组患者手术及术后指标比较

统计值P值手术时间/min术中出血量/mL Harris量表评分术前术后1 d术后3个月Rasmussen评分术前术后1 d术后3个月PTSA(°)术后1 d术后3个月MPTA(°)术后1 d术后3个月双钢板组(n=29)48.50±13.12 75.35±6.18单钢干板组(n=25)47.00±13.29 73.97±14.01 1.482 1.240>0.05>0.05 43.28±11.64 49.45±11.38a 87.40±16.95a 43.54±11.78 49.23±15.65 82.36±11.24 0.635 0.721 6.143>0.05>0.05<0.05 5.30±1.12 17.42±5.81 17.23±6.45 5.46±1.94 15.35±1.48 15.36±1.58 0.578 5.387 5.046>0.05<0.05<0.05 8.63±0.22 8.95±0.45 7.30±0.36 7.56±0.59 5.087 5.342<0.05<0.05 88.65±1.44 89.70±1.95 80.74±1.74 81.17±1.88 10.354 11.347<0.05<0.05
两组患者术后,胫骨内侧平台骨折伴骨折脱位神经损伤、延迟愈合、畸形愈合及并发症发生总数比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。及时处理了所有患者并发症。(表3、表4)
表3 两组患者术后出现并发症数量比较[n(%)]
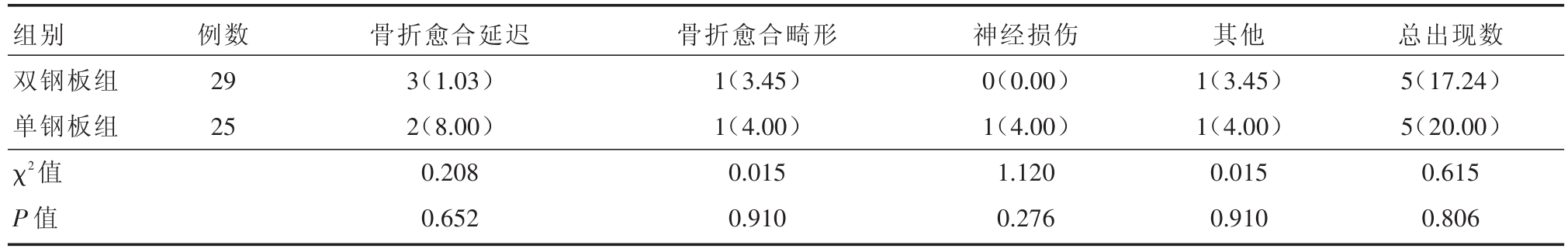
组别双钢板组单钢板组χ2值P值例数29 25骨折愈合延迟3(1.03)2(8.00)0.208 0.652骨折愈合畸形1(3.45)1(4.00)0.015 0.910神经损伤0(0.00)1(4.00)1.120 0.276其他1(3.45)1(4.00)0.015 0.910总出现数5(17.24)5(20.00)0.615 0.806
表4 两组患者术后并发症随访资料
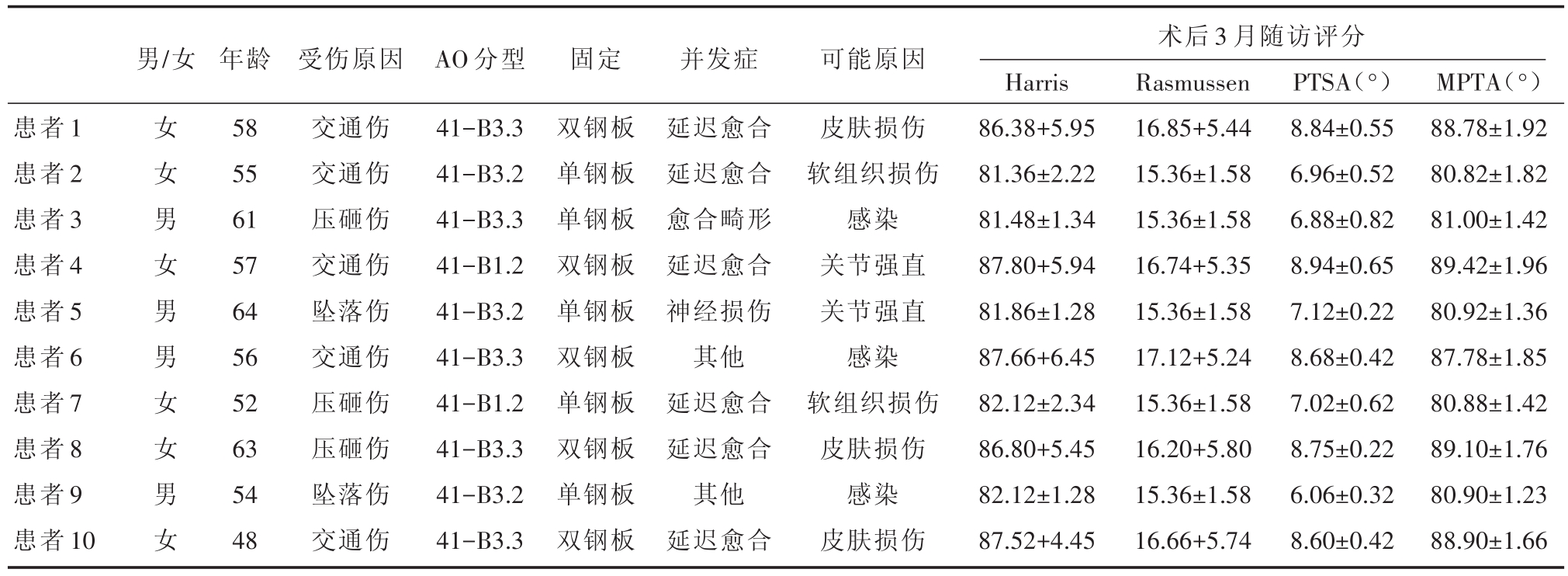
男/女术后3月随访评分患者1患者2患者3患者4患者5患者6患者7患者8患者9患者10女女男女男男女女男女年龄58 55 61 57 64 56 52 63 54 48受伤原因交通伤交通伤压砸伤交通伤坠落伤交通伤压砸伤压砸伤坠落伤交通伤AO分型41-B3.3 41-B3.2 41-B3.3 41-B1.2 41-B3.2 41-B3.3 41-B1.2 41-B3.3 41-B3.2 41-B3.3固定双钢板单钢板单钢板双钢板单钢板双钢板单钢板双钢板单钢板双钢板并发症延迟愈合延迟愈合愈合畸形延迟愈合神经损伤其他延迟愈合延迟愈合其他延迟愈合可能原因皮肤损伤软组织损伤感染关节强直关节强直感染软组织损伤皮肤损伤感染皮肤损伤Harris 86.38+5.95 81.36±2.22 81.48±1.34 87.80+5.94 81.86±1.28 87.66+6.45 82.12±2.34 86.80+5.45 82.12±1.28 87.52+4.45 Rasmussen 16.85+5.44 15.36±1.58 15.36±1.58 16.74+5.35 15.36±1.58 17.12+5.24 15.36±1.58 16.20+5.80 15.36±1.58 16.66+5.74 PTSA(°)8.84±0.55 6.96±0.52 6.88±0.82 8.94±0.65 7.12±0.22 8.68±0.42 7.02±0.62 8.75±0.22 6.06±0.32 8.60±0.42 MPTA(°)88.78±1.92 80.82±1.82 81.00±1.42 89.42±1.96 80.92±1.36 87.78±1.85 80.88±1.42 89.10±1.76 80.90±1.23 88.90±1.66
胫骨平台骨折属于膝关节面的骨折,手术治疗为该骨折的首选方法。手术治疗面临的第一个技术问题是切口的选择。常用的方法为内、外侧切口,最早由Georgiadis等人提出实施双钢板双切口入路[8],即:若患者存在髁骨折,则需增加前侧或后侧一个切口。①膝前内侧和后内侧作双切口的优缺点:前内侧切口较大,后内侧切口较小,依次分别处理前部骨折和内侧骨折块,双切口不足以保证7 cm宽度的皮桥,若后内侧切口较小,骨折部位难以暴露,操作视野空间小,复位固定操作易失败,术后导致瘢痕挛缩,膝关节屈伸功能受到影响。②本文采用的是膝关节内侧单切口,其优缺点:直视下骨折复位,骨折部位临时固定后,膝关节曲膝位,牵开股薄肌和半膜肌,获得较大空间便于内侧钢板的置入,固定“内侧柱”操作方便;牵开腓肠肌与半腱肌间隙,暴露“后内侧柱”,通过双钢板对两个层面上骨折块进行复位并固定,对后内侧骨折块,形成一个三维的钢形梁状固定架,阻止骨折处向后内侧移位可能,极大提高膝关节生物力学稳定性[9],避免了小切口容易造成胫神经、腘动静脉的损伤风险。同时,降低膝关节继发移位及术后僵硬等并发症的发生率,对术后早期恢复功能性锻炼更为有利,该种术式有2个问题应当重视:①隐神经伴行大隐静脉走形,切开深筋膜后,注意寻找并保护之。②屈膝位时牵开股薄肌、半膜肌后,安装钢板如有难度,再适度分离鹅足腱膜的止点,若过度分离,会导致膝关节的稳定性降低[10]。
膝关节骨折患者关节面遭破坏,滑膜、韧带组织损伤,术后出现炎性反应粘连、滑囊消失及纤维化,长期制动造成的肌力萎缩,导致膝关节功能障碍,为此,术中内固定的稳定程度与膝关节功能呈正相关。当前,临床上尚无较好、公认地处理膝关节胫骨内侧平台骨折伴脱位的术式[11,12]。前内侧入路,采用钢板联合螺钉前、后位拉力固定,是目前临床上应用较多的方法,对骨折端行进内固定,手术方便安全,避免多个切口损伤血管或神经现象。但该术式存在的短板:①骨折部位暴露的视野局限,后内侧骨折块处理的不甚理想;②屈曲膝关节时,螺钉对该部位固定力,不足于拮抗膝关节后内侧部位遇到剪切应力,术后,患者膝关节固定不稳或股骨内侧髁半脱位移到后下方的现象偶有发生[13]。还需要注意2个问题:①尽可能避免内侧半月板前角损伤;②拉力螺钉固定时,螺纹一定要长于骨折线,遇到骨折线偏向外侧情况,螺钉加上垫片后再固定,固定会牢固可靠[14]。
本文临床实践研究表明:采用双钢板内侧入路内固定术式,治疗胫骨内侧平台骨折伴脱位患者,可获得更好的治疗效果。手术的体会和经验:①术前,为患者影像学和体格全面检查,重点了解受伤部位和毗邻有无血管损伤和韧带破坏,以免术中出现意外和被动。一定要消肿治疗,降低皮肤张力后,再行手术缝合;②术中,尽量减少大隐静脉皮下剥离,对术后伤口愈合有利;对比健侧,保持患侧下肢力线,减少或避免因固定不稳造成的畸形愈合等现象;③术后,为使减轻患肢肿胀程度,血液回流顺畅,使用弹力绷带。
综上,胫骨内侧平台骨折伴骨折脱位的治疗,采用双钢板内侧入路内固定,是一种有效固定和维持膝关节力线手术方法。
[1] 王军,赵春鹏,李庭,等.骨折脱位型胫骨平台骨折发生率及内侧和后内侧骨块影像学特点[J].中华创伤杂志,2015,31(5):427-430.
[2] 毛玉江,张伯松,公茂琪,等.200例胫骨平台骨折的骨折形态及损伤机制分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2016,18(1):47-51.
[3] Sabesan VJ,Danielsky PJ,Childs A,et al.Multiligamentknee injuries with associated tibial plateau fractures:A report of two cases[J].World JOrthop,2015,6(3):363-368.
[4] 李煜,刘玉民,张宁,等.胫骨平台骨折Schatzker分型与膝关节功能相关性分析[J].重庆医学,2016,45(12):1629-1631.
[5] 冯刚,潘志军,李杭,等.双锁定钢板交叉支撑固定治疗累及后外侧的C3型胫骨平台骨折[J].中华骨科杂志,2014,34(7):695-702.
[6] Ebrahimzadeh MH,Birjandinejad A,Moradi A,et al.Clinical instability of the knee and functional differences following tibial plateau fractures versus distal femoral fractures[J].Trauma Mon,2015,20(1):e21635.
[7] 顾海伦,杨军,丁立峰,等.改良后内侧倒L形入路在胫骨平台后柱骨折手术中的应用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2016,31(8):836-840.
[8] Pun TB,Krishnamoorthy VP,Poonnoose PM,et al.Outcome of schatzker type Ⅴ and Ⅵ tibial plateau fractures[J].Indian J Orthop,2014,48(1):35-41.
[9] 洪顾麒,吕天润,陈群,等.三切口入路治疗累及后侧平台的复杂胫骨平台骨折[J].中华骨科杂志,2017,37(12):705-710.
[10] Cho JW,Kim J,Cho WT,et al.Approaches and fixation of the posterolateral fracture fragment intibial plateau fractures:a review with an emphasis on rim plating via modifiedanterolateral approach[J].Int Orthop,2017,41(9):1887-1897.
[11] Hung YW,Ko WS,Liu WH,et al.Local review of treatment of hand enchondroma(artificial bone substitute versus autologous bone graft) in a tertiary referral centre:13 years′experience[J].Hong Kong Med J,2015,21(3):217-223.
[12]蒋煜青,黄健,郭伟康,等.外侧前后联合入路双钢板内固定治疗累及后外髁的胫骨外侧平台骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2017,19(4):340-344.
[13]陈希聪,司徒晓鹏,劳永.锁定加压钢板治疗复杂胫骨平台骨折82例临床研究[J].岭南现代临床外科,2012,12(2):128-129.
[14] Liu GY,Xiao BP,Luo CF,et al.Results of a modified posterolateral approach for the isolated posterolateral tibialplateau fracture[J].Indian JOrthop,2016,50(2):117-120.
The efficacy of two operative methods in patients with medial tibial plateau fracture and fracture dislocation
中图分类号: