

岭南现代临床外科 ›› 2020, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (02): 205-209.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-976X.2020.02.015
摘要:
延迟愈合、骨不连、伤口感染和伤口裂开是胫骨远端骨折最常见的并发症,其原因是胫骨远端的生理特性、血供不足和前方肌肉覆盖少。因此,胫骨远端骨折的理想治疗方法仍存在争议[1,2]。近年来,微创经皮钢板接骨术(minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis,MIPPO)以其技术优势和良好的临床效果得到了广泛的应用[3],具有手术时间短、失血少、软组织损伤小、骨折区感染率低、肢体早期活动可能性高、钢板取出后同一区域其他骨折的发生率降低,植骨需求少等优点[2,4,5],但 MIPPO术后可能由于延迟愈合,可能导致钢板断裂[6]。髓内钉(intramedullary nailing,IMN)技术也是治疗各种长骨骨折常用方法。由于骨-髓内钉产生摩擦力,IMN不仅能稳定抗弯和抗旋转,而且也能够减少骨愈合过程中的再次骨折。但是,当椎管直径大于髓内钉直径时,更容易发生对线不良和旋转。阻挡螺钉(Poller螺钉)的设计可作为辅助复位工具,能够预防或纠正胫骨和股骨干干骺端骨折IMN的对位对线不良[7-9]。本文选取我院单侧胫骨干中下段骨折患者178例,探讨交锁髓内钉联合阻挡螺钉固定的应用效果,并比较MIPPO和IMN治疗型胫骨远端骨折的疗效。
选取我院单侧胫骨干中下段骨折患者178例(2017年4月~2019年6月),将采用MIPPO术治疗的88例作为对照(MIPPO组),将采用交锁髓内钉穿钉联合阻挡螺钉固定治疗的90例作为IMN+阻挡螺钉组(IMN+阻挡螺钉)。MIPPO组女48例,男40例;年龄18~68岁,平均(42.81±12.33)岁;骨折侧别:37例右侧,51例左侧;致伤原因:55例交通事故伤,20例高处坠落伤,13例重物压伤;AO分型:14例42-A,42例42-B,32例42-C。IMN+阻挡螺钉组女51例,男39例;年龄18~70岁,平均(44.06±12.52)岁;骨折侧别:35例右侧,55例左侧;致伤原因:56例交通事故伤,18例高处坠落伤,16例重物压伤;AO分型:17例42-A,43例42-B,30例42-C。两组年龄、性别、骨折侧别、致伤原因、AO分型等基线资料均衡可比(P>0.05)。
纳入标准:患者知情、自愿并签署同意书;经X线扫描证实为单侧胫骨干中下段骨折;年龄≥18岁;生命体征正常。排除标准:伴有其他部位严重骨折或创伤;双侧骨折;伴有血液系统疾病、严重骨质疏松、重要脏器异常、麻醉及手术禁忌证;胫骨既往接受过手术治疗;合并骨不连、病理性骨折、陈旧性骨折。
MIPPO组采用MIPPO术治疗,全身麻醉,取屈髋、屈膝位,常规消毒、铺巾;自内踝突出位置做纵行切口(3~4 cm),将胫骨远端内侧充分暴露,沿其进行钝性分离,形成皮下隧道,将钢板由隧道置入;在骨折线附近使用1枚螺钉固定,C臂机透视下确认钢板位置满意,使用锁定螺钉导向器钻孔,拧入锁定螺钉;经C臂机确认螺钉固定良好,且骨折复位满意,最后关闭切口。
IMN+阻挡螺钉组采用交锁髓内钉闭合穿钉联合阻挡螺钉固定治疗,全身麻醉,取屈髋、屈膝位,常规消毒、铺巾;通过手法牵引复位骨折部位,在骨折远端轴位畸形的凹面靠近骨折线处钉入阻挡螺钉,后进行扩髓并拧入螺钉,借助C臂机确认骨折复位,髓内钉顶尖旁再钉入阻挡螺钉1枚;利用瞄准器在远近端各置入2枚锁钉,经C臂机确认螺钉固定良好,且骨折复位满意,最后关闭切口。典型案例见图1、图2。术后2 d内给予抗感染治疗,2 d后进行功能锻炼。
比较两组优良率,其中骨折愈合,未发生严重并发症,关节活动正常为优;骨折愈合,下肢无畸形,未发生神经、血管损失等并发症,关节活动度恢复>75%为良;骨折愈合,下肢轻微畸形,出现轻度并发症,关节活动度恢复51%~75%,对抗力量受限为中;未达上述标准为差[5]。比较两组手术及术后指标(术中出血量、手术时间、术后恢复时间、骨折愈合时间),骨折愈合即指骨折处无压痛、叩痛,活动正常,骨折线模糊,在无辅助情况下下肢能在平地持续步行3 min以上且超过30步[6]。比较两组术前、术后3个月胫骨干Johner-Wruhs评分(100分)、踝关节Kofoed评分(100分)、膝关节Baily评分(50分),评分越高功能恢复越好[7]。比较两组术后并发症发生率,包括畸形愈合、切口感染、延迟愈合等。
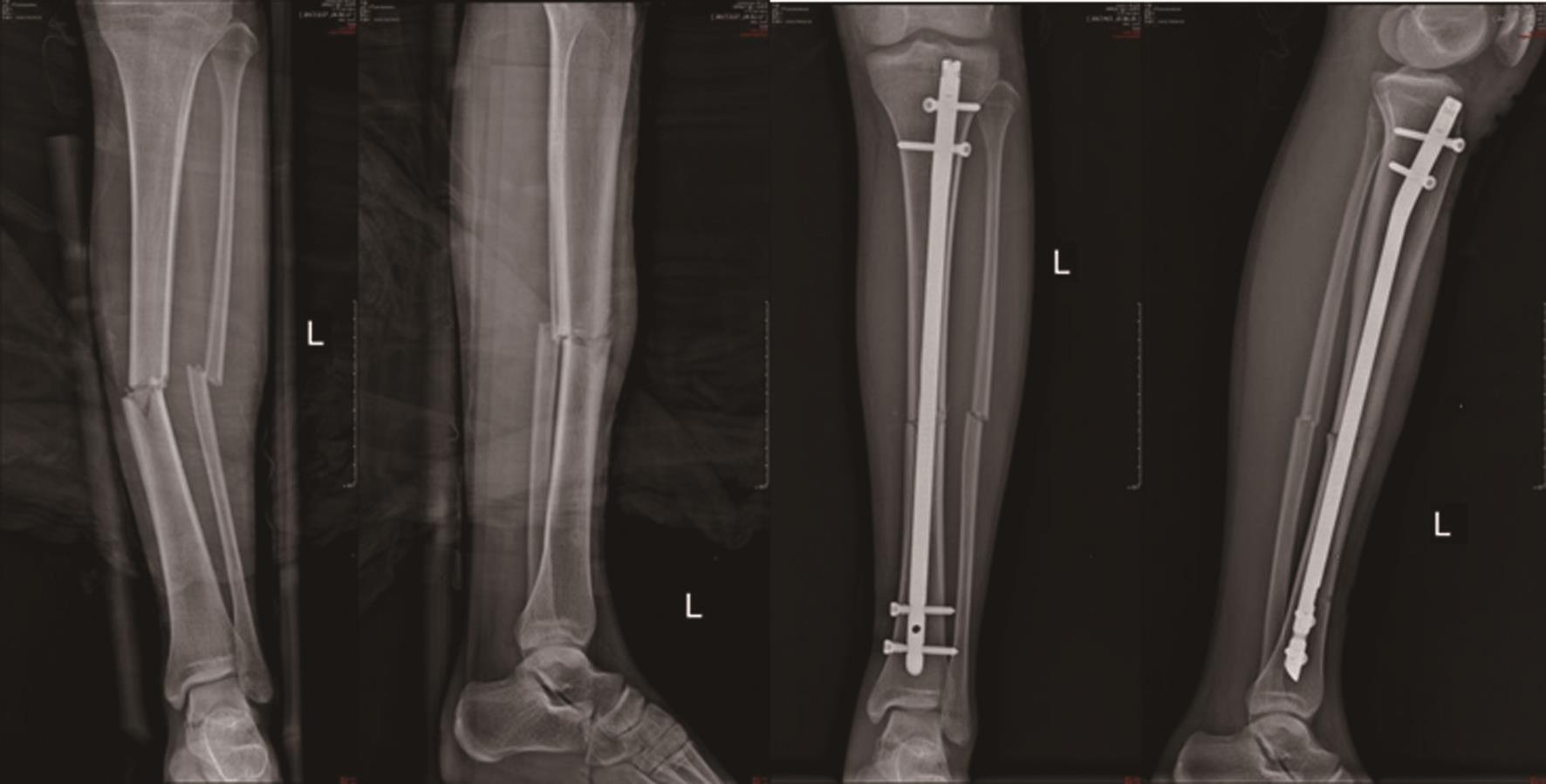
图1 术前正、侧位图(左图)、交锁髓内钉闭合穿钉联合阻挡螺钉固定术后正、侧位图(右图)
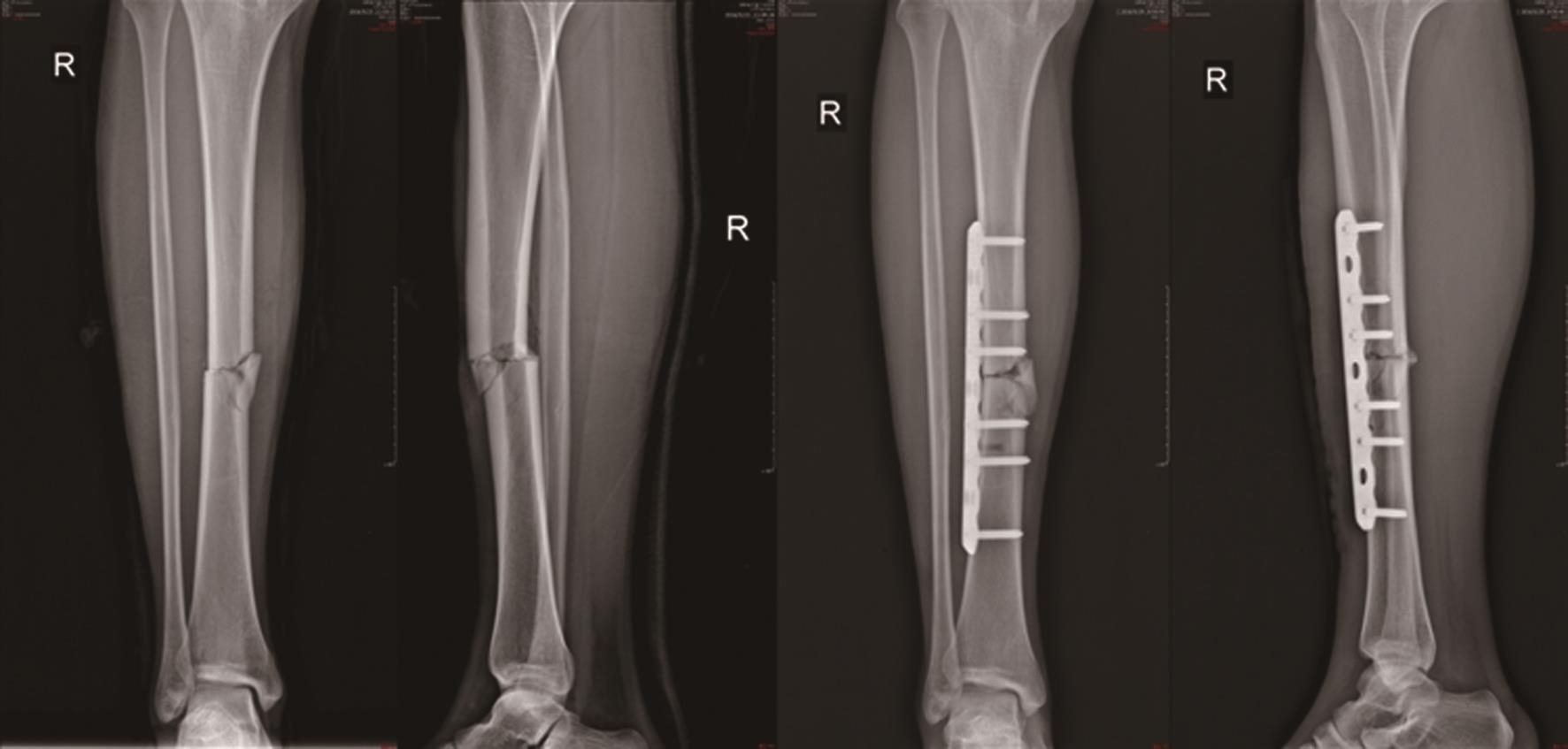
图2 术前正、侧位图(左图)、MIPPO术后正、侧位图(右图)
通过SPSS 22.0分析数据,计量资料以(x±s)表示,行t检验,计数资料以n(%)表示,行χ2检验,P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
两组优良率比较,IMN+阻挡螺钉组96.67%高于MIPPO组84.09%(P<0.05),见表1。
表1 两组疗效对比[n(%)]

优良中差组别IMN+阻挡螺钉组MIPPO组χ2值P值例数90 88 69(76.67)64(72.73)18(20.00)10(11.36)3(3.37)14(15.91)0(0.00)0(0.00)优良率87(96.67)74(84.09)8.146 0.004
IMN+阻挡螺钉组术中出血量多于MIPPO组,手术时间长于MIPPO组,术后恢复时间、骨折愈合时间短于MIPPO组(P<0.05),见表2。
表2 手术及术后指标(x±s)
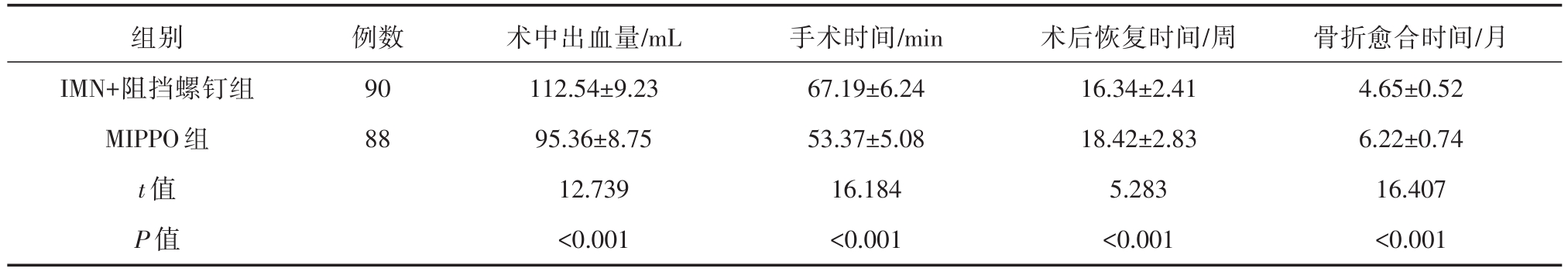
组别IMN+阻挡螺钉组MIPPO组t值P值例数90 88术中出血量/mL 112.54±9.23 95.36±8.75 12.739<0.001手术时间/min 67.19±6.24 53.37±5.08 16.184<0.001术后恢复时间/周16.34±2.41 18.42±2.83 5.283<0.001骨折愈合时间/月4.65±0.52 6.22±0.74 16.407<0.001
术前,两组胫骨干Johner-Wruhs评分、踝关节Kofoed评分、膝关节Baily评分比较无明显差异(P>0.05);术后3个月,IMN+阻挡螺钉组胫骨干Johner-Wruhs评分、踝关节Kofoed评分、膝关节Baily评分均高于MIPPO组(P<0.05),见表3。
表3 胫骨干、踝关节、膝关节功能(x±s,分)

组别 例数IMN+阻挡螺钉组MIPPO组t值P值90 88 Johner-Wruhs术前55.44±10.41 56.87±10.56 0.910 0.364术后3个月87.33±11.57 80.08±10.71 4.336<0.001 Kofoed术前45.68±10.22 47.15±10.29 0.956 0.340术后3个月86.13±12.04 79.86±11.47 3.556 0.001 Baily术前14.72±2.69 15.16±2.72 1.085 0.279术后3个月41.97±7.72 35.36±7.44 5.815<0.001
IMN+阻挡螺钉组术后并发症发生率3.33%,低于MIPPO组19.32%(P<0.05),见表4。
表4 术后并发症发生率[n(%)]

组别IMN+阻挡螺钉组MIPPO组χ2值P值例数90 88畸形愈合1(1.11)7(7.95)切口感染1(1.11)4(4.55)延迟愈合1(1.11)6(6.82)总发生率3(3.33)17(19.32)11.399 0.001
胫骨骨折是下肢最常见的骨折,胫骨远端骨折约占所有胫骨骨折的10%~13%,常伴有软组织损伤[10]。如果不及时进行适当的治疗,这些骨折可能会导致患者严重残疾。MIPPO和IMN被认为是治疗胫骨远端骨折最常用的两种方法,但都有较高的并发症。
MIPPO与传统开放式钢板方法比较,能够明显降低伤口并发症和深部感染[29,30],MIPPO 能够保护骨折后局部血肿对骨痂形成的存在和骨的营养动脉,同时防止医源性软组织损伤。伤口并发症的发生率和愈合时间取决于除手术技术外的其他因素,包括患者的健康状况、皮肤和软组织污染、手术室条件以及手术时机。有研究报道伤口并发症通常会延迟伤口愈合过程。在中国香港进行的一项研究报告,在接受MIPPO固定的胫骨远端骨折患者中,15%的晚期感染率为[11],并且由于皮肤撞击而去除了52%的患者的植入物。此外,在本研究中,由于MIPPO间接复位技术复杂,MIPPO手术时间较长[11]。文献报道IMN组和MIPPO组的愈合延迟、骨不连、畸形愈合等并发症相似[12]。IMN可减少骨外血供,允许负荷分担,避免广泛的软组织剥离[13]。但是,在IMN治疗中,必须高度重视远端钉内固定的技术难点,胫骨远端骨折的外固定可能导致复位不足、不愈合和骨髓腔感染[1]。Wang等[1]在 MIPPO与 IMN治疗胫骨远端骨折的meta分析中,IMN的手术时间和术后愈合时间均较MIPPO短,MIPPO有较高的创面并发症的发生率,两组愈合过程中的并发症和深部感染的发生率没有统计学意义的差别。总体上,接受IMN治疗的患者可能会有稍好的结果。
本组病例中,髓内钉钉联合阻挡螺钉固定治疗胫骨干中下段骨折中,在垂直于交锁钉平面且紧贴髓内钉部位置入1~2枚螺钉,缩小髓腔,可使髓内钉在复位骨折时正确进入远端中心,而阻挡螺钉的使用能防止术后患者活动中髓内钉松动,达到稳定髓内钉的作用[14]。相关研究指出,阻挡螺钉与髓内钉联合应用,可使髓内钉更加接近于干骺端皮质骨,提升远期复位效果[15]。本研究发现,IMN+阻挡螺钉组优良率高于MIPPO组,术中出血量多于MIPPO组,手术时间长于MIPPO组,术后恢复时间、骨折愈合时间短于MIPPO组,术后3个月胫骨干Johner-Wruhs评分、踝关节Kofoed评分、膝关节Baily评分均高于MIPPO组(P<0.05),提示交锁髓内钉闭合穿钉联合阻挡螺钉固定治疗单侧胫骨干中下段骨折,可提高优良率,改善胫骨干、踝关节、膝关节功能,促进康复。骨折愈合时间短的原因主要在于髓内钉弹性固定可保证其侧方与成角移位,提高固定稳定性,促进骨折愈合[16]。本研究还发现,IMN+阻挡螺钉组术后并发症发生率低于MIPPO组(P<0.05),提示交锁髓内钉闭合穿钉联合阻挡螺钉固定治疗单侧胫骨干中下段骨折安全性高。原因在于MIPPO术切口较大,插入钢板会挫伤软组织,增加感染风险,且胫骨远端髓腔宽,而髓内钉细,闭合复位效果不理想。此外,应用交锁髓内钉闭合穿钉联合阻挡螺钉固定应注意:远端粉碎性骨折作为其禁忌证,不建议使用髓内钉固定。
综上,交锁髓内钉闭合穿钉联合阻挡螺钉固定治疗单侧胫骨干中下段骨折,可提高优良率,改善胫骨干、踝关节、膝关节功能,降低并发症发生率,促进康复。
[1] Wang B,Zhao Y,Wang Q.Minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis versus intramedullary nail fixation for distal tibial fractures:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J].J Orthop Surg Res,2019,14(1):456.
[2] Andalib A,Sheikhbahaei E,Andalib Z,Tahririan MA.Effectiveness of Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis(MIPO)on Comminuted Tibial or Femoral Fractures[J].Arch Bone Jt Surg,2017,5(5):290-295.
[3] Zhiquan A,Bingfang Z,Yeming W,et al.Minimally invasive plating osteosynthesis(MIPO)of middle and distal third humeral shaft fractures[J].J Orthop Trauma,2007,21:628-633.
[4] Bolhofner BR,Carmen B,Clifford P.The results of open reduction and Internal fixation of distal femur fractures using a biologic(indirect)reduction technique.J Orthop Trauma,1996,10(6):372-7.
[5] Johnson EE.Combined direct and indirect reduction of comminuted four-part intraarticular T-type fractures of the distal femur[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,1988,(231):154-162.
[6] Rüedi TP,Sommer C,Leutenegger A.New techniques in indirect reduction of long bone fractures[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,1998,347:27-34.
[7] Krettek C,Miclau T,Schandelmaier P,et al.The mechanical effect of blocking screws(“Poller screws”)in stabilizing tibia fractures with short proximal or distal fragments after insertion of small-diameter intramedullary nails[J].J Orthop Trauma,1999,13(8):550-553.
[8] Hannah A,Aboelmagd T,Yip G,Hull P.Anovel technique for accurate Pollercblocking screw placement[J].Injury,2014,45(6):1011-1014.
[9] Fu B.Locked META intramedullary nailing fixation for tibial fractures via a suprapatellar approach[J].Indian J Orthop,2016,50:283-289.
[10] Newman SD,Mauffrey CP,Krikler S.Distal metadiaphyseal tibial fractures[J].Injury,2011,42(10):975-984.
[11] Lau TW,Leung F,Chan CF,Chow SP.Wound complication of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal tibia fractures[J].Int Orthop,2008,32(5):697-703.
[12] Goh EL,Chidambaram S,Eigenmann D,et al.Minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis versus intramedullary nail fixation for closed distal tibial fractures:a meta-analysis of the clinical outcomes[J].SICOT J,2018,4:58.
[13] Nork SE,Schwartz AK,Julie A,et al.Intramedullary nailing of distal metaphyseal tibial fractures[J].J Bone Joint Surg Am Vol,2005,87:1213.
[14] 郭志民,龚星星,王瑛,等.交锁髓内钉内固定治疗胫骨多节段骨折的疗效[J].中华创伤杂志,2017,33(2):171-174.
[15] 徐新立,杨林.交锁髓内钉闭合穿钉联合阻挡螺钉固定治疗胫骨干中下段骨折疗效评价[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2019,12(7):533-537.
[16] 喻景奕,周公社,位新维,等.阻挡钉快速置入技术在闭合复位交锁髓内钉内固定治疗胫骨远侧干骺端骨折中的应用[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2019,21(2):127-132.
Analysis of the efficacy and safety of interlocking intramedullary nail closed and nailing combined with blocking screw for treatment of patients with unilateral tibial fracture
中图分类号: