

岭南现代临床外科 ›› 2019, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (06): 746-750.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-976X.2019.06.023
摘要:
腹部切口感染多见于腹部术后,是外科术后最多的并发症,也是医院感染的重要组成部分。腹部切口感染常规的治疗方法是拆除缝线、敞开切口、伤口换药、选择敏感抗菌药物,根据伤口肉芽情况再予以二期缝合[1,2]。负压封闭引流技术(VSD)能够及时的清理创面渗出物、改善血供、防止伤口二次感染和感染清洁伤口,同时减少患者换药痛苦,降低住院费用,已被广泛应用于感染性伤口[3-5]。而芒硝作为一种传统中草药,具有治疗腹泻、便秘、清热消肿等功效。现代医学研究表明芒硝溶液外敷可以加快感染性皮肤伤口处淋巴细胞、内皮细胞及成纤维细胞生成,有消肿、缓解疼痛和促进创面新鲜肉芽生长的作用[6,7]。因此,我们将芒硝溶液持续滴注和负压封闭引流技术联合治疗难愈合的腹部感染性伤口,尝试为临床治疗腹部感染性伤口提供更加经济有效的新方法,现报道如下。
收集2018年1月至2018年12月南昌大学第二附属医院胃肠外科和中山大学附属第六医院胃肠、疝和腹壁外科收治的腹会阴部手术后出现伤口感染且较难愈合,伤口清创后予以负压封闭引流术的80例患者。收入观察标准:①在26~60岁之间;②术后出现切口部位缺损,发热,体温达38.0~39.5℃;③血常规炎症指标明显升高者;④切口部位细菌培养阳性。排除标准:①肝肾功能严重损害;心肺功能不全;②全身营养情况较差。出院标准:患者伤口基本愈合,无感染或其他并发症。根据治疗方法,将其分为2组,试验组(VSD+芒硝液)40例,男24例,女16例,年龄为(36.6±4.6)岁;对照组(VSD)40例,男28例,女12例,年龄为(35.8±3.9)岁,两组患者之间性别、年龄、清创手术时间、既往病史等均无统计学差异(P>0.05)(表1)。
表1 两组患者基本特征比较
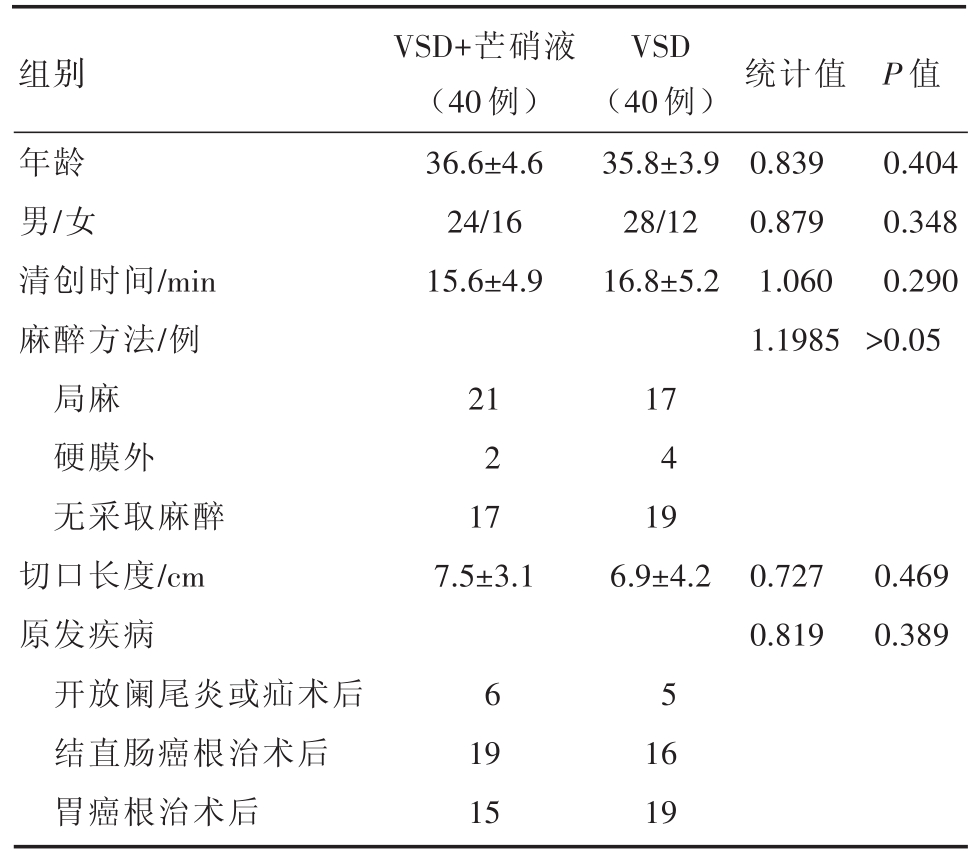
组别统计值P值年龄男/女清创时间/min麻醉方法/例局麻硬膜外无采取麻醉切口长度/cm原发疾病开放阑尾炎或疝术后结直肠癌根治术后胃癌根治术后VSD+芒硝液(40例)36.6±4.6 24/16 15.6±4.9 VSD(40例)35.8±3.9 28/12 16.8±5.2 0.839 0.879 1.060 1.1985 0.404 0.348 0.290>0.05 21 2 17 7.5±3.1 17 4 19 6.9±4.20.727 0.819 0.469 0.389 6 5 19 15 16 19
两组患者均行腹会阴部手术,术后3~6天内出现手术切口部位感染,需拆除缝线,伤口清创且无法一期缝合。
术前将200 g芒硝晶体溶解于2000 mL灭菌注射用水中,使其浓度达0.1 g/mL,于常温保存;完善相关术前准备后,根据患者伤口感染大小、严重程度、患者疼痛忍受能力等情况采取局部麻醉、椎管内麻醉、无需麻醉的方式;伤口经碘伏溶液、双氧水、生理盐水依次冲洗,然后开始清创,清创过程中,清除伤口感染坏死组织,切去边缘感染皮肤,彻底清理皮下坏死组织、线结、残腔基底创面,直至可见新鲜肉芽组织,然后用过氧化氢溶液、生理盐水以此反复冲洗手术区域,直至创面无残留坏死组织、异物、分泌物等,以盐水纱布覆盖创面。
试验组:根据创面大小选择合适的海绵敷料(武汉维斯第医用科技有限公司生产),完整覆盖于清创后伤口,用皮钉固定VSD海绵敷料四周,然后用透明敷贴完整覆盖,连同硅胶引流管,检查有无漏气,患者返回病房后,将VSD通过负压吸引管连接引流储存罐,用另一根负压引流管将储存罐与床头中心负压瓶相连,持续125~200 mmHg(1 mmHg=0.133 kPa)负压吸引,VSD引流管侧孔连接输液器,另一端接入术前配制的0.1 g/mL芒硝溶液持续滴注。使用过程中,检查VSD海绵状敷料是否积液,引流管是否处于负压状态,引流管有无堵塞,VSD创面有无漏气或异味,并根据情况做相应处理。
对照组:VSD使用情况同实验组,VSD侧孔引流管连接输液器,给予滴注2 000 mL生理盐水。两组患者治疗期间均给予敏感抗生素治疗,同时根据引流管有无堵塞以及创面情况,一般4至6天清理创面,更换VSD敷料海绵,观察伤口愈合情况。
观察记录两组患者冲洗过程中的一般资料,定期观察两组患者伤口情况,包括伤口渗液、伤口深度、残腔、肉芽生长等情况,记录术后患者疼痛缓解情况(详见表2)、在相同时间内创面肉芽组织生长情况(详见表3)、伤口达二期缝合时间、伤口缝合后基本愈合时间、伤口愈合后再次感染率、换药总费用等。
表2 疼痛缓解情况的视觉模拟评分法

注:使用疼痛尺让患者根据疼痛程度,滑动背面尺子上的游标,研究者从正面读出疼痛数值
疼痛程度无痛轻微疼痛,能忍受疼痛并影响睡眠,尚能忍受逐渐强烈的疼痛,疼痛难忍剧烈疼痛评分(分)0 1-3 4-6 7-9 10
采用SPSS 23.0统计软件对所有记录指标进行统计学分析。其中计量资料的统计结果表示方法采用均数±标准差,计数资料比较采用卡方检验。计量资料比较采用t检验,以P<0.05表示有统计学意义。
表3 创面肉芽组织生长情况评分
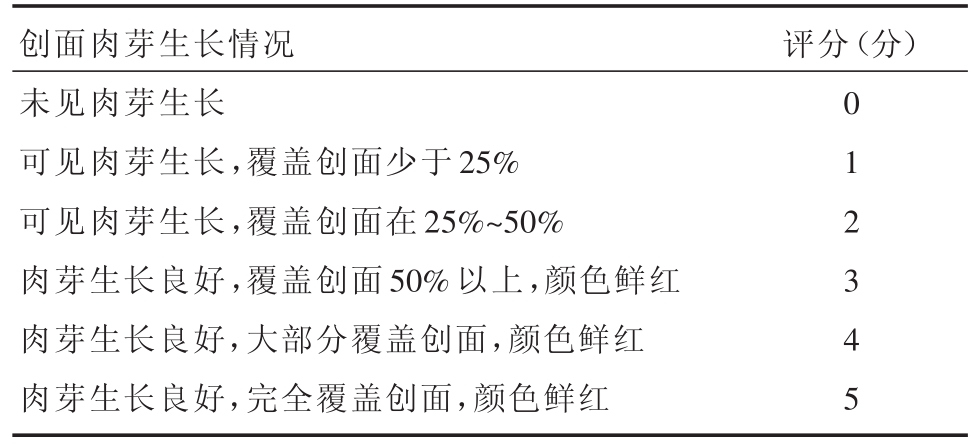
创面肉芽生长情况未见肉芽生长可见肉芽生长,覆盖创面少于25%可见肉芽生长,覆盖创面在25%~50%肉芽生长良好,覆盖创面50%以上,颜色鲜红肉芽生长良好,大部分覆盖创面,颜色鲜红肉芽生长良好,完全覆盖创面,颜色鲜红评分(分)0 1 2 3 4 5
患者感染性伤口经清创后,有肉芽组织覆盖,后因各种原因创面脓胎再次出现,敷料存在异味;或患者创面经二期缝合后,伤口再次出现红肿、脓性分泌物渗出、敷料有异味等情况,我们视为伤口再次感染。本次研究中,试验组19例创面长度不超过5 cm患者经过更换1次引流敷料后伤口直接愈合,18例患者经过更换2次或以上引流敷料后二期缝合,伤口经6~8天后愈合,2例患者经清创后第一次更换敷料观察伤口时发现创面大量脓胎覆盖、有明显异味,需二次清创,考虑第一次清创不彻底,负压引流不畅导致伤口再次感染;1例结肠癌术后造口患者伤口经过二期缝合后,伤口再次出现红肿,有脓性分泌物,敷料有异味,考虑造口距离切口较近,造口护理不当,导致伤口再次感染。对照组14例创面长度不超过5 cm患者经过更换1次引流敷料后伤口直接愈合,16例患者经过更换2次或以上引流敷料后二期缝合,伤口经9~11天后愈合,4例患者经过二次清创,2例患者经过3次清创,4例胃肠道术后患者伤口经二期缝合后,由于营养状态不良,饮食欠佳,合并糖尿病史,伤口愈合不良。
两组患者在每次更换负压吸引装置时,观察创面肉芽组织情况,两组患者经清创引流后感染均较前明显减轻,创面可见肉芽组织生长,但试验组患者创面肉芽组织覆盖率评分(3.97±0.42)明显高于对照组(2.25±0.44)。
更换敷料时观察患者创面,待创面出现大量新鲜肉芽组织且无明显分泌物后,冲洗引流液清亮,未见明显浑浊时给予二期缝合,避免过早缝合,造成伤口再次感染。记录两组伤口愈合时间发现,试验组伤口达愈合时间(11.75±1.69天)和缝合后愈合时间(7.15±1.63天)较对照组伤口愈合时间(16.4±2.74天)和缝合后愈合时间(10.27±2.89天)明显缩短,两组结果有统计学意义(P<0.05)(表4),试验组患者经过芒硝持续滴注冲洗后,创面能够更加快速的愈合,住院时间大大缩短。
患者经清创后,评估患者术后伤口疼痛情况,根据表2细则评分,试验组患者术后疼痛评分(2.87±0.36)较对照组(4.05±0.85)明显减轻,疼痛缓解时间明显缩短;患者出院后统计换药总费用发现,试验组患者因换药次数较对照组少,费用明显减少,两组患者实验结果有统计学意义(P<0.05)(表4)。
表4 两组患者观察指标疗效比较
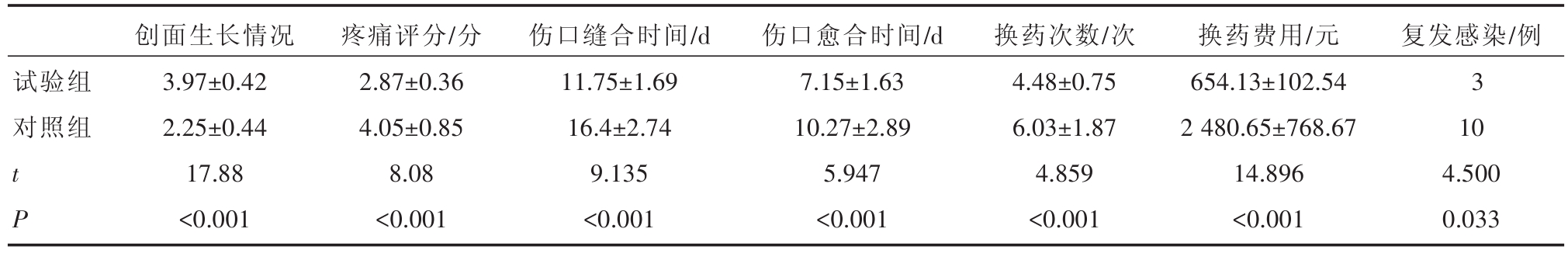
试验组对照组t P创面生长情况3.97±0.42 2.25±0.44 17.88<0.001疼痛评分/分2.87±0.36 4.05±0.85 8.08<0.001伤口缝合时间/d 11.75±1.69 16.4±2.74 9.135<0.001伤口愈合时间/d 7.15±1.63 10.27±2.89 5.947<0.001换药次数/次4.48±0.75 6.03±1.87 4.859<0.001换药费用/元654.13±102.54 2 480.65±768.67 14.896<0.001复发感染/例3 10 4.500 0.033
腹部感染性伤口在多种因素的作用下,创面血液循环欠佳,大量毒害物质以及分泌物长期淤积在创面,导致细菌大量繁殖,严重阻碍伤口的愈合[8,9]。然而常规处理方法增加住院时间的同时,也会增加患者换药痛苦及住院费用,浪费医护人员工作精力及医院医疗卫生资源,还易诱发产生医患矛盾,因此,临床上需要一种简单有效,安全经济的治疗方法。
1992年Fleischmann博士首先将负压封闭引流技术应用于四肢急性和感染性创面的处理,并取得了显著的疗效。1994年裘华德教授首次将创面负压封闭引流技术应用于普通外科手术以及感染坏死性创面的治疗,在临床上取得了广泛的认可[10]。感染性创面经过清创后可以在持续负压吸引的作用下改善局部血供,减轻组织水肿,还可以起到机械牵拉作用[11,12]。透明敷贴可以隔绝创面与外界,有效地防止污染和交叉感染。由于VSD往往不能够及时的将坏死组织及渗出液引流,导致毒害物质堆积,反而加重感染,创面无法愈合。因此,最新研究在VSD的基础上放置一条溶液输入管,改良成为新型负压封闭吸引-滴注冲洗系统(VSD-instill,VSD-i)[13,14]。
感染性创面经过清创后使用输液管持续滴注引流,可以时刻保持创面相对清洁,抑制细菌生长。创面经过持续机械性的冲洗,能够及时的清除创面脓性分泌物及毒害物质,避免创面持续的感染,同时由于坏死分泌物被冲走,破坏细菌生长环境。置管冲洗还能够减轻创伤表面张力,提高血供,改善局部缺氧,从而减少厌氧菌的繁殖,有利于创面肉芽组织的快速覆盖,从而减少换药次数和再次感染机会[15-17]。抗生素的使用无疑是外科治疗感染性伤口的重要环节,但随着广谱抗生素的大量使用,耐药菌株不断增加,这也导致感染性伤口成为目前治疗的难点[18,19]。芒硝最早记载于《别录》,具有治疗便秘、腹泻、清热消肿等多种功效。传统医药研究表明芒硝具有一定的消肿止痛,促进伤口再生功效[20]。张晓秋等研究发现277例腹部手术伤口经芒硝外敷治疗后,92.9%患者的手术伤口愈合速度和愈合程度显著提升,且预后瘢痕收缩期明显缩短[21]。由此,在VSD的基础上,我们使用芒硝溶液持续滴注,与传统生理盐水滴注对比并评估其疗效。我们发现将芒硝溶液持续滴注和VSD技术联合治疗难愈合的腹部感染性伤口,可以减少分泌物对创面的刺激,促进创面肉芽组织的快速生长,有利于伤口的早期愈合,同时减轻患者的痛苦,减少患者住院费用。因此,芒硝溶液持续滴注结合负压封闭引流技术较生理盐水冲洗具有止痛、减轻感染、降低炎症反应、促进肉芽组织快速生长等优点,可以通过加快肉芽组织生长速度来缩短感染性伤口二期缝合时间,有利于伤口早期的愈合,避免抗菌药物长期使用的同时降低细菌耐药性,为临床治疗腹部感染性伤口提供了一种更加经济有效的新方法。
[1] Yoshioka T,Kondo Y,Fujiwara T.Successful wound treatment using negative pressure wound therapy without primary closure in a patient undergoing highly contaminated abdominal surgery[J].Surg Case Rep,2018,4(1):85.
[2] Edmiston CE,McBain AJ,Kiernan M,et al.A narrative review of microbial biofilm in postoperative surgical site infections:clinical presentation and treatment[J].J Wound Care,2016,25(12):693-702.
[3] Chen X,Liu L,Nie W,et al.Vacuum Sealing Drainage Therapy for Refractory Infectious Wound on 16 Renal Transplant Recipients[J].Transplant Proc,2018,50(8):2479-2484.
[4] DeFazio MV,Economides JM,Anghel EL,et al.Tractionassisted internal negative pressure wound therapy with bridging retention sutures to facilitate staged closure of high-risk wounds under tension[J].Wounds,2017,29(10):289-296.
[5] 宗振,江志鹏,侯泽辉,等.自制负压封闭引流装置治疗腹股沟疝术后补片感染疗效分析[J].中国实用外科杂志,2016,36(05):569-570.
[6] 朱茄英,陈茶花,鄢小莲,等.大黄加芒硝导泻治疗有机磷农药中毒的效果观察[J].中国危重病急救医学,2012,24(6):346-348.
[7] 刘绍龑,白明,杨亚蕾,等.芒硝外用抗炎作用研究[J].中华中医药杂志,2012,27(02):312-315.
[8] Tastaldi L,Petro CC,Krpata DM,et al.History of surgical site infection increases the odds for a new infection after open incisional hernia repair[J].Surgery,2019,166(1):88-93.
[9] Kirkpatrick AW,Roberts DJ,Faris PD,et al.Active negative pressure peritoneal therapy after abbreviated laparotomy:the intraperitoneal vacuum randomized controlled trial[J].Ann Surg,2015,262(1):38-46.
[10]裘华德,王彦峰.负压封闭引流技术介绍[J].中国实用外科杂志,1998,18(4):41-42.
[11] Liu J,Hu F,Tang J,et al.Homemade-device-induced negative pressure promotes wound healing more efficiently than VSD-induced positive pressure by regulating inflammation,proliferation and remodeling[J].Int J Mol Med,2017,39(4):879-888.
[12]Virani SR,Dahapute AA,Bava SS,et al.Impact of negative pressure wound therapy on open diaphyseal tibial fractures:A prospective randomized trial[J].J Clin Orthop Trauma,2016,7(4):256-259.
[13]Hu N,Wu X H,Liu R,et al.Novel application of vacuum sealing drainage with continuous irrigation of potassium permanganate for managing infective wounds of gas gangrene[J].J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci,2015,35(4):563-568.
[14]Moreno D,Conde AJ,Lorono G,et al.Comparison of the volume of root canal irrigant collected by 2 negative pressure needles at different flow rates of delivery[J].J Endod,2018,44(5):838-841.
[15]Ousey K,Cutting KF,Rogers AA,et al.The importance of hydration in wound healing:reinvigorating the clinical perspective[J].JWound Care,2016,25(3):122,124-130.
[16]Olufemi OT,Adeyeye AI.Irrigation solutions in open fractures of the lower extremities:evaluation of isotonic saline and distilled water[J].SICOT J,2017,3:7.
[17]Fernandez L,Ellman C,Jackson P.Use of negative pressure wound therapy with instillation in the management of complex wounds in critically ill patients[J].Wounds,2019,31(1):E1-E4.
[18]Berrios-Torres SI,Umscheid CA,Bratzler DW,et al.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Guideline for the Prevention of Surgical Site Infection,2017[J].JAMA Surg,2017,152(8):784-791.
[19]Sisay M,Worku T,Edessa D.Microbial epidemiology and antimicrobial resistance patterns of wound infection in Ethiopia:a meta-analysis of laboratory-based cross-sectional studies[J].BMCPharmacol Toxicol,2019,20(1):35.
[20]王熙,刘帮华,黄德铨,等.芒硝溶液坐浴治疗混合痔术后切口水肿疗效观察[J].山西中医,2013,29(01):50-51.
[21]陈小青,项贤美.芒硝外敷治疗术后伤口感染35例[J].中国药业,2013,22(4):80-81.
Application study of continuous infusion of glauconite solution combined with vacuum sealing drainage(VSD)in the treatment of infected abdominal wounds
中图分类号: